How to create an effective advertising campaign in Google ADS: A step-by-step guide for beginners
- Overview of the advertising account creation process
1.1 Why it is important to have a separate advertising account
1.2 Step-by-step instructions for creating a Google Ads account
1.3 Setting up payment information and first checks - How to set up a campaign based on business goals
2.1 Defining business goals
2.2 Types of campaigns based on goals
2.3 Setting up a campaign based on goals - Choosing an audience, keywords and ads
3.1 How to choose the right audience
3.2 How to choose keywords
3.3 How to create effective ads
3.4 A/B testing of ads - Budget recommendations for starting
4.1 How to determine the optimal starting budget
4.2 How to choose a budget for different types of campaigns
4.3 Budget allocation between campaigns
4.4 How to avoid wasting budget
4.5 Optimizing CPC (cost per click) costs
4.6 Real case: budget optimization for a local business - Optimizing campaigns after launch
5.1 Analyzing key metrics
5.2 Using A/B testing
5.3 Optimizing keywords
5.4 Optimizing ad copy and design
5.5 Controlling budget and costs
5.6 Analyzing competitors
1. Overview of the advertising account creation process
Google Ads is a powerful tool for attracting new customers. But like any tool, it works best when set up correctly. In this section, we’ll take a detailed look at how to create your first ad account and avoid common mistakes.
1.1. Why it is important to have a separate advertising account
Many entrepreneurs start using Google Ads from a shared Google account that they also use for email or other services. This can create issues with access, analytics, and financial calculations.
The advertising account must be separate in order to:
- Ensure cost transparency. All advertising campaigns, their results and costs will be collected in one place.
- Make it easier to collaborate with marketing agencies. You can share access to your account without revealing personal data.
- Ensure data security. If you use a shared account, there is a risk of losing access due to a security breach.
“My business has reached new heights since I started using a separate ad account. It has allowed me to analyze campaigns in a more structured way and avoid chaos.”
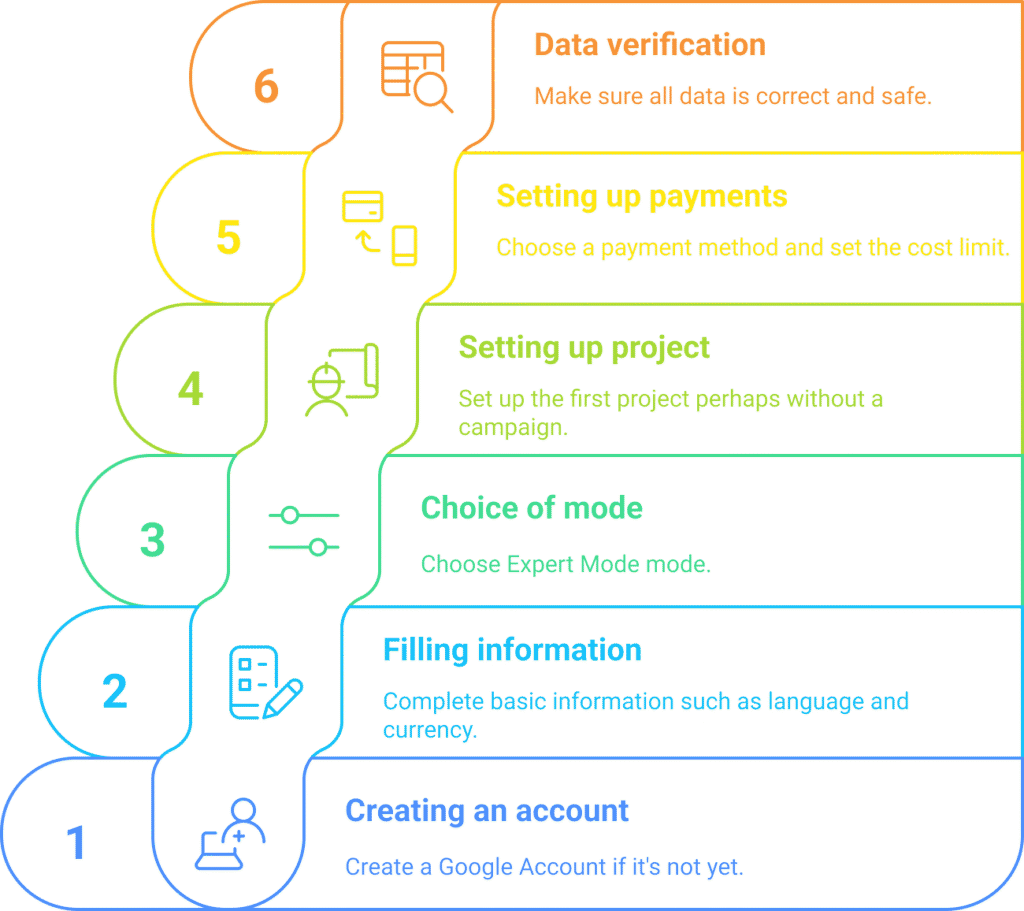
1.2. Step-by-step instructions for creating a Google Ads account
- Create a Google Account (if you don’t already have one).
This is the first step to getting started with Google Ads. Sign in to ads.google.com with your account. - Fill in your basic information.
After signing in to Google Ads, you’ll be asked to provide:- Language and time zone (it is important to choose the correct one, as it cannot be changed after setting).
- The currency in which you plan to make payments.
- Select the operating mode: “Expert Mode.”
Google often offers a simplified “beginner mode,” but it has limited functionality. For full access to the settings, it is better to select “Expert Mode” right away. - Set up your first project.
Google will prompt you to create a campaign. For a test run, you can select “Create without a campaign” to set up the interface and billing information first.
“It is important to choose the correct time zone and currency. An entrepreneur who chose the wrong time zone got confused with the launch time of the advertisement and lost money.”
1.3. Setting up payment details and first checks
To start advertising, you’ll need to add your payment information. The process is simple, but there are a few things you should keep in mind:
- Choose a payment method. Google accepts credit cards, PayPal, and direct bank transfers. The most convenient method for most people is a credit card.
- Set a spending limit. You can set a maximum amount you plan to spend per month. This will help you avoid overspending.
After setting up your payment information, check:
- Are all details entered correctly?
- Whether you have expense notifications enabled (Google can send them to your email).
- Is two-factor authentication enabled for account security?
Example to explain:
A business owner with a small budget ($300 per month) set a spending limit in Google Ads. One day, due to a configuration error, the campaign was spending more than expected. Thanks to the spending limit, the system stopped the campaign when the spending reached the limit.
“Advertising campaigns work best when every stage of their launch is controlled. Setting limits helps avoid unexpected costs.”
Creating an advertising account in Google Ads is the first step to a successful advertising campaign. The main thing is to pay attention to details, such as choosing the operating mode, correctly setting up payment details, and following basic security rules. Properly preparing your account will save time and help avoid mistakes in the future.
2. How to set up a campaign based on your business goals
Creating a Google Ads campaign is the foundation of your advertising strategy. The success of your advertising depends on how well you define your business goals and incorporate them into your settings. In this section, we’ll look at how to clearly define your goals and turn them into an effective advertising strategy.
2.1 Defining business goals
Every business has unique challenges that need to be addressed through advertising. Before launching a campaign, it’s important to answer the key question: “What do I want to achieve?”
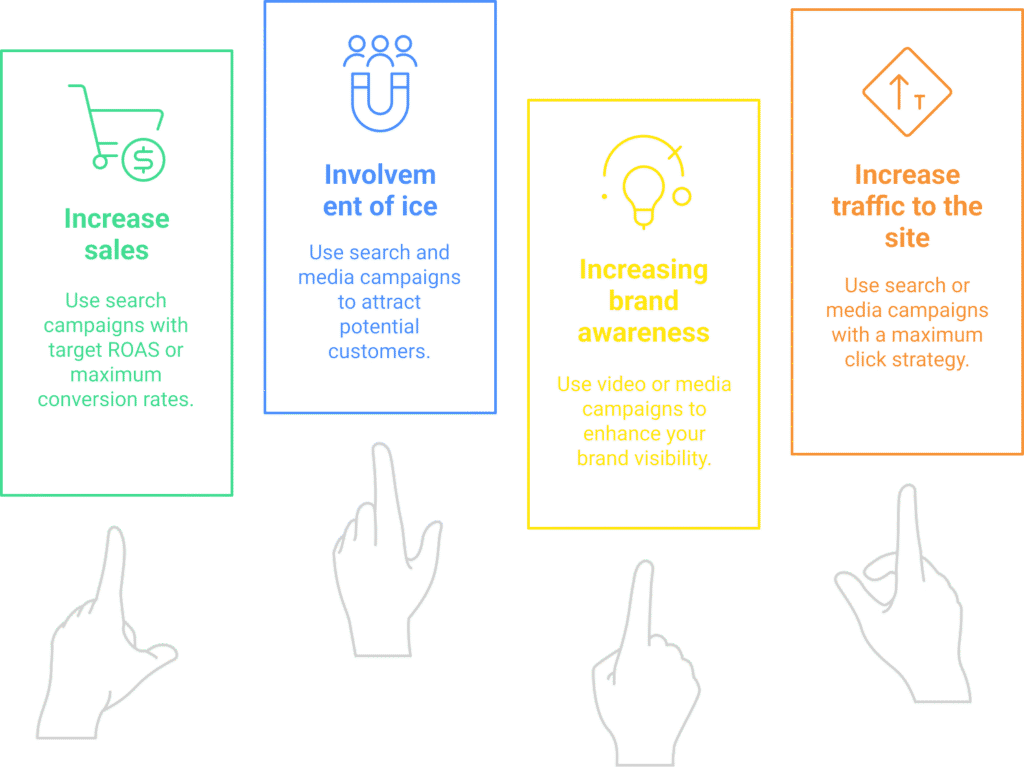
The main goals of advertising campaigns:
- Increase sales. For example, an online store seeks to attract customers to a new collection of products.
- Attracting potential customers (leads). This may be necessary for companies that offer services (repairs, consulting, etc.).
- Increasing brand awareness. Especially relevant for new companies or products on the market.
- Increase website traffic. This helps businesses that want to attract more visitors for conversions or outreach.
How to define a goal for your campaign?
- Analyze your business needs. For example, if you have a promotion on a product, your goal is sales. If you are opening a new store, you need recognition.
- Prioritize. What is more important right now: sales or brand awareness? Focus on one goal.
- Consider seasonality. For example, campaigns to increase sales are most often launched before the holidays.
“My business experienced a drop in customers during the summer. With a clear goal in mind, I set up a campaign focused on summer discounts and brought customers back.”
2.2 Campaign types depending on goals
Once you have your goal in mind, you need to choose the appropriate campaign type. Google Ads offers several formats, each suited to specific tasks.
Campaigns to increase sales
Best choice: search campaigns.
- Benefits: They show ads in response to users’ search queries. For example, if someone searches for “buy a laptop,” your ad will appear at the top of the results.
- Bidding strategies: Choose target return on ad spend (ROAS) or maximize conversions to optimize your spend.
Example:
An online electronics store launched a search campaign to promote discounted laptops. As a result, 70% of clicks from the ad converted into sales.
Campaigns to attract potential customers (leads)
Best choice: search and display campaigns.
- Search campaigns will help you reach people who are already interested in your services.
- Display campaigns can attract those who haven’t yet searched for your product but are potentially interested.
“Display advertising allowed me to expand my client base. We used banners that led to a form for requesting a consultation.”
Brand awareness campaigns
Best choice: video campaigns or display campaigns.
- Video advertising on YouTube is a great tool for emotional impact. It allows you to present your brand through a story or a unique idea.
- Display campaigns work through visual banners that remind people of your product even after visiting your site.
Example:
A new sportswear brand launched a video campaign with the slogan “Choose comfort every day.” The commercials were viewed by over 500,000 people, and traffic to the site tripled.
Campaigns to increase website traffic
Best choice: search or display campaigns.
- Use the “Maximum Clicks” strategy to get more visitors.
- Use dynamic ads that automatically substitute relevant keywords and ads.
“After setting up a campaign to increase traffic, we achieved a significant increase in website traffic, which helped increase sales.”
2.3 Setting up a campaign according to your goals
Once you know what your goal is, follow these steps:
- Choose a campaign type. Choose a search, display, shopping, or video campaign based on your goals.
- Set a target action. This could be a sale, a click, or a form fill-out.
- Optimize your bids. For beginners, automated strategies like Target Conversions work best .
- Test. Run a campaign with a small budget and see how it performs. If you’re not happy with the results, make changes to your settings.
“Testing allows you to find the perfect campaign setup. I started with $50 and was able to identify the most effective keywords for my business.”
Setting up an advertising campaign that meets your business goals requires understanding your objectives and familiarity with Google Ads tools. If you define your goal correctly, choose the appropriate campaign type and strategy, your advertising investment will definitely bring results.
3. Selecting your audience, keywords, and ads

This section covers three key aspects that determine the success of your advertising campaign: choosing the right audience, carefully selecting keywords, and creating effective ads. All of these elements work together to make your ads relevant, visible, and effective.
3.1 How to choose the right audience
Audience is the foundation of any advertising campaign. You can have great ads and perfect keywords, but if your ads aren’t reaching the right audience, they won’t perform well.
Why is it important to know your audience?
Google Ads allows you to target people with extreme precision. For example, you can reach people based on geographic location, demographics (age, gender, interests), or behavioral characteristics (like those who have recently searched for your products).
Steps to define your audience:
- Create a portrait of your ideal client. Who is he? What is his age, income, profession?
- Study user behavior. How do your customers search for your products or services?
- Use tools. Google Ads has an “Audiences” section that helps you identify interested users.
“I targeted ads to users aged 25-40 with an interest in electronics. This allowed me to double my CTR compared to ads for a general audience.”
An example of effective audience selection
A sports equipment company launched an advertising campaign targeting users interested in fitness and an active lifestyle. Thanks to precise targeting, they were able to attract customers who were already interested in exercise equipment and increase sales.
3.2 How to choose keywords
Keywords are the bridge between users’ search queries and your ads. Choosing the right keywords can help ensure that your ads are seen by the people who really need them.
Step-by-step process for selecting keywords:
- Keyword research: Use the Google Keyword Planner tool to find relevant queries for your business.
- Choose different types of keywords.
- Common words. For example, “buy a laptop.”
- Long keywords. For example, “buy a laptop for a programmer.”
- Negative keywords: These exclude irrelevant impressions, such as “free.”
The role of negative keywords
Adding negative keywords will help you avoid wasting your budget. For example, if you sell premium products, add the word “cheap” as a negative.
“After adding negative keywords, the number of low-quality clicks decreased by 30%, and the cost of conversions became lower.”
Example: choosing the right keywords
A food delivery cafe chose the following keywords: “pizza delivery”, “cheese pizza”, “order pizza home”. Negative words included “pizza recipe” and “how to make pizza”. This allowed them to reduce irrelevant impressions.
3.3 How to create effective ads
Ads are the face of your advertising campaign. How compelling they are can determine whether a user will click on your ad.
What makes an ad effective?
- Relevance. The ad should match the user’s query. If a person is searching for “buy a smartphone,” your ad should include that query.
- Value: State why the user should choose you (for example, free shipping or 20% off).
- Call to action (CTA). Phrases like “Buy Now,” “Learn More,” and “Order Today” encourage action.
“We added a call to action, ‘Sign up now and get a discount,’ and our ad’s CTR increased by 15%.”
Using ad extensions
Google Ads allows you to add extensions to make your ad more informative:
- Links to sections of the site. For example, “About us”, “Contacts”.
- Prices: This helps users see the cost of products at a glance.
- Additional information. For example, “Free shipping on orders over 1000 UAH.”
Example of an effective ad
Online store advertising:
“Handmade leather bags. Free shipping on orders over 1000 UAH. Buy today – get a 15% discount. [Place an order]”
3.4 A/B testing of ads
Don’t limit yourself to just one ad variation. Use multiple versions and test them to find the most effective one.
Choosing your audience, keywords, and ads are strategic steps that affect the results of your advertising campaign. By knowing your audience, choosing the right words, and creating compelling ads, you can significantly increase your advertising effectiveness and achieve your goals.
- Change the text. Test different headlines, descriptions, and calls to action.
- Check different keywords. For example, compare “Buy smartphone” with “Order phone online.”
- Measure your results. Examine your CTR, conversions, and costs to understand what works best.
“A/B testing helped us understand that a headline with the call to action “Order today – get a discount” works better than a general product description.”
Choosing your audience, keywords, and ads are strategic steps that affect the results of your advertising campaign. By knowing your audience, choosing the right words, and creating compelling ads, you can significantly increase your advertising effectiveness and achieve your goals.
4. Budget recommendations for starting out
Advertising budget is one of the key aspects of planning a Google Ads campaign. Improper allocation of funds can lead to rapid budget depletion without proper results. In this section, we will take a detailed look at how to optimally plan a budget in the initial stages, avoid common mistakes, and ensure maximum return on investment.
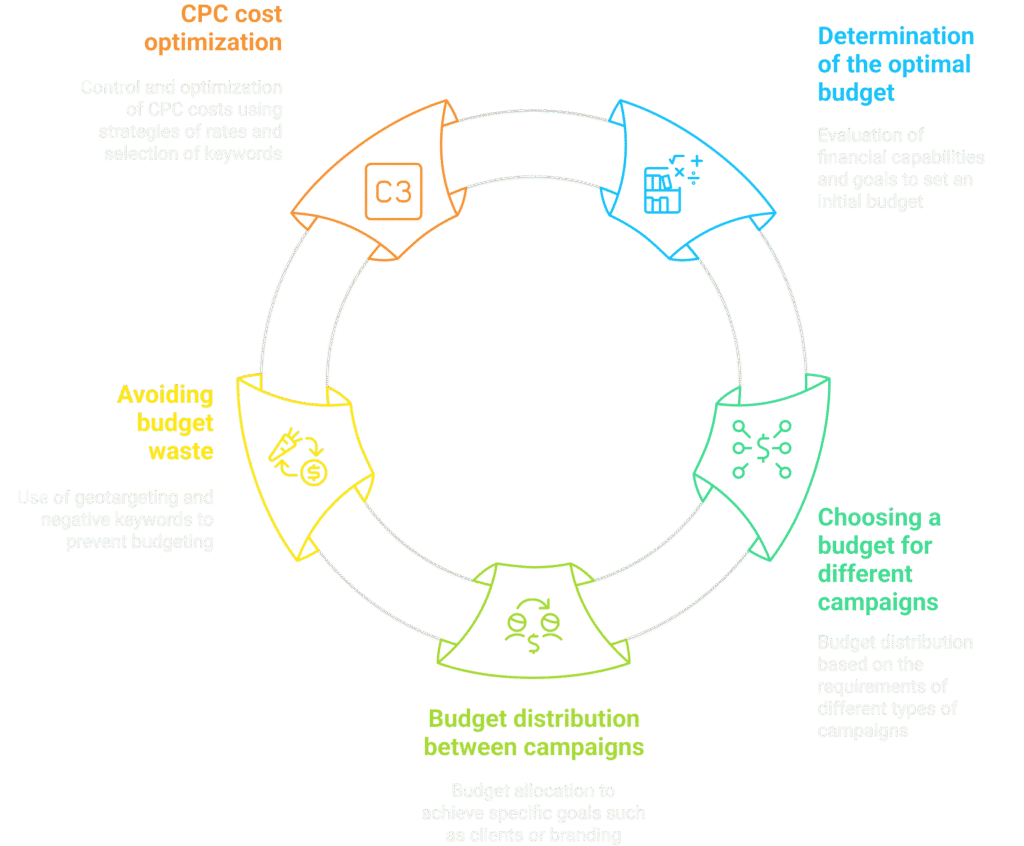
4.1 How to determine the optimal starting budget
Assessment of financial capabilities and goals
Before setting a budget, consider:
- What revenue do you expect to get from advertising?
- What volume of customers do you want to attract?
- How much are you willing to invest without risk for your business?
Practical example:
A sportswear company has calculated that each new customer brings them an average of UAH 500 in profit. Having set a budget of UAH 5,000, they expect to attract at least 10 new customers.
“Understanding our average revenue per client allowed us to adjust our budget so that we didn’t overspend, but we also didn’t lose potential profit.”
Tips for beginners
- Start with a small budget. This will allow you to test the effectiveness of your campaign without taking on too much risk.
- Use a daily budget as a cost control tool. For example, set 100-200 UAH per day to gradually study audience behavior.
4.2 How to choose a budget for different campaign types
Different campaigns have different budget requirements.
- Search advertising. Often requires a smaller budget because it focuses on specific queries. For example, for a local business, 1000–3000 UAH per month may be enough.
- Media advertising. Requires more funds due to a larger audience and wider reach. To start, plan from 3000–5000 UAH.
- YouTube advertising. The minimum budget can start from 5,000 UAH, as video advertising is often more expensive, but has a high level of engagement.
“When we launched the campaign on YouTube, we set a budget of 5,000 UAH. This allowed us to get 50,000 views and 2,000 clicks in the first two weeks.”
4.3 Budget allocation between campaigns
Budget allocation depends on your goals. For example:
- Customer acquisition: Allocate more money to search advertising, as it brings the most conversions.
- Branding: Invest in display and video advertising to reach a wide audience.
Practical strategy:
If your total budget is 10,000 UAH:
- 60% on search advertising.
- 30% on media advertising.
- 10% for testing new formats, such as video advertising.
4.4 How to avoid wasting your budget
Use geotargeting
Your ads should only be shown to people in your targeted geographic area. For example, if you only work in Kyiv, it doesn’t make sense to show ads across Ukraine.
Work with negative keywords
Add words that exclude impressions to irrelevant audiences. For example, “free” if you only offer paid services.
“After adding the negative keyword ‘free’, my low-quality click costs decreased by 20% and the number of relevant customers increased.”
Analyze the results
Check your campaign metrics regularly. If a keyword is consuming a lot of budget but not converting, change your strategy or replace it.
4.5 CPC (cost per click) cost optimization
What is CPC and how to control it?
CPC (cost per click) is the amount you pay for each click on your ad. A high CPC can quickly drain your budget if your campaign is set up incorrectly.
CPC optimization tips:
- Set a maximum acceptable CPC. If your average conversion brings in 100 UAH of profit, the CPC should not exceed 10–20 UAH.
- Focus on low-competition keywords. For example, instead of “buy smartphone,” use “buy gaming smartphone.”
- Automated bidding strategies: Use Maximize clicks if your goal is to drive traffic, or Target cost per conversion if your focus is on sales.
4.6 Real case: budget optimization for a local business
A women’s clothing store decided to launch Google Ads with a budget of UAH 3,000 per month. The strategy included:
- Geotargeting only to your city.
- Using long-tail keywords, for example, “women’s wedding dresses in Kyiv.”
- Regular analysis and disabling of irrelevant keywords.
Result: after a month, conversions increased by 40%, and advertising costs remained within budget.
Optimal budget management is about balancing costs with expected results. Start small, test different strategies, analyze results, and refine your approaches. With the right strategy, even a small budget can yield tangible results.
5. Optimizing campaigns after launch
Advertising with Google Ads is not just about setting up campaigns. Even the best-configured campaigns need regular analysis and adjustments to achieve maximum performance. In this section, we’ll look at how to optimize campaigns, avoid common mistakes, and learn from audience behavior to improve results.
5.1 Analysis of key metrics
To evaluate the effectiveness of your Google Ads campaign, you need to regularly review the following metrics:
- CTR (Click-Through Rate) is a measure of how engaging your ads are. If your CTR is below average (around 2% for search campaigns), it could indicate a problem with your ad text or keyword selection.
- CPC (Cost Per Click) — price per click. A high CPC can quickly eat up your budget, so it’s worth comparing it to the average revenue per client.
- Conversions and CPA (Cost Per Acquisition) — the number of conversions and their cost. These are the main metrics that show how well your campaign is meeting your business goals.
“After reviewing the metrics, we realized that the CTR of one of the ads in the display campaign was half as low as expected. We changed the text and added a call to action, and the CTR increased to 3.5%.”
5.2 Using A/B testing
A/B testing is a way to determine which of your ads performs better. Create two versions of your ad with slight differences (text, image, call to action) and see which one gets more clicks or conversions.
Example:
Ad A: “Buy stylish furniture with a 20% discount. Order now!”
Ad B: “Modern furniture for your home. 20% discount! Buy today!”
After a week of data analysis, it became clear that version A had a CTR of 4.2%, while version B had only 3.5%. This allowed them to focus on a more effective ad format.
5.3 Keyword Optimization
Regularly analyze the search queries that trigger your ads. Use these strategies:
- Adding new keywords: When analyzing search terms, you may find new words that are converting but weren’t added initially.
- Use negative keywords. Exclude irrelevant queries that “eat up” your budget. For example, if you only sell new smartphones, add the word “used” to your negative keyword list.
“We found that our ad was being triggered by the query ‘free design template’, even though we only offer paid services. Adding ‘free’ to the negative keywords helped us avoid unnecessary costs.”
5.4 Optimizing ad text and design
Your ads should be as relevant as possible to your target audience. If you are getting clicks but conversions remain low, check:
- Does the ad text match the content of the page the user is landing on?
- Is the call to action clear and compelling?
- Can the visual part of the ad (for display advertising) be improved?
5.5 Budget and cost control
Once you’ve launched your campaign, it’s important to monitor how your budget is being used. If your costs are increasing but your results are stable, it’s a sign that you need to make changes.
- Reallocate budget: If one campaign is generating more conversions than another, shift more funds to the successful campaign.
- Use automated strategies: Switch to Target CPA or Maximize conversions to let Google Ads algorithms allocate your budget more efficiently.
“After a month of manual management, we switched to the ‘Target CPA’ strategy. This helped reduce the cost of acquiring a customer from 150 to 120 UAH, without changing the overall budget.”
5.6 Competitor analysis
See how competitors advertise:
- What keywords do they use?
- What style of ads do they work with?
This can be done using specialized tools such as SEMrush or Ahrefs.
Case study:
While analyzing our competitors, we noticed that they were using ads with offers like “Free Shipping.” By adding this to our ad, we got 20% more clicks in a week.
Optimizing your campaigns after launch is an ongoing process. Each analysis and adjustment allows you to reduce costs, improve results, and get the most out of your advertising. Remember, Google Ads is not a magic tool, but a system that requires attention and improvement.



